Quick Answer...
Inverter Generator vs Generator: What’s The Difference?
Inverter generators are great for clean power, saving fuel, and running quietly. They’re perfect for sensitive electronics and for fun activities like camping. They are also generally smaller and easier to carry and store.
On the other hand, traditional generators can provide more power and are better for heavy tasks or backup power at homes, businesses or on building sites.
Introduction To Inverter Generator Vs Generator
If you’ve ever found yourself wondering about the differences between inverter generators and conventional generators, you’re not alone. In today’s world, where portable power is a necessity for many, understanding the distinctions between these two types of generators is crucial.
Inverter generators and conventional generators may serve the same purpose, but they have distinct characteristics that set them apart. From their fuel efficiency to their noise levels, this article will explore the key differences between these two types of generators, helping you make an informed decision when it comes to selecting the right one for your needs.
Power Generation Basics
Inverter Generator Vs Generator: Generation Basics
Power generation is the process of converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. Generators play a crucial role in power generation by providing a reliable source of electricity in various settings.
Whether you’re camping in the great outdoors or facing a power outage at home, understanding the basics of how generators work and the different types available can help you make an informed decision.
How do generators work?
Generators utilize the principle of electromagnetic induction to produce electricity. They consist of two main components: a prime mover and an alternator. The prime mover, which can be an engine powered by gasoline, diesel, or natural gas, converts chemical or mechanical energy into rotational motion. The alternator then converts rotational motion into electrical energy through the use of electromagnetic induction.
In simpler terms, the prime mover powers the alternator, which generates electricity through the interaction of magnets and an electrical conductor. As the prime mover spins the alternator, an electrical current is created and can be used to power lights, appliances, and other electrical devices.
What are the different types of generators?
Generators can be broadly classified into two main categories: conventional generators and inverter generators. While both types serve the purpose of generating electricity, they have significant differences in terms of their working principles, power output, portability, parallel operation capabilities, applications, maintenance requirements, costs, and environmental impact. Let’s explore these differences in detail.
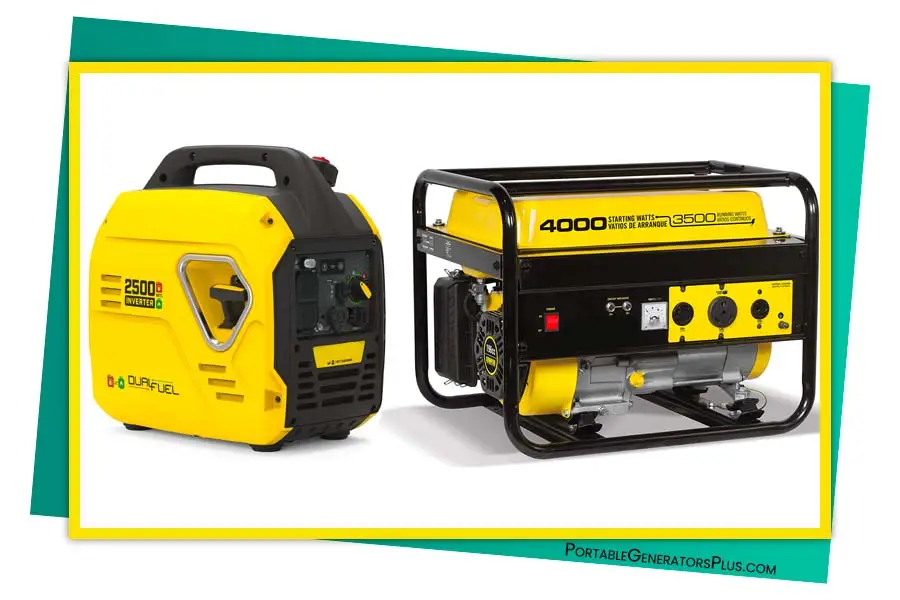

Conventional Generators
Inverter Generator Vs Generator: Traditional Generators
Conventional generators, also known as standard or traditional generators, have been the go-to choice for decades. They employ a simple design that has stood the test of time.
Working Principle
Conventional generators generate electricity at a fixed frequency of 60 Hz (or 50 Hz in some countries). They produce alternating current (AC) that is directly proportional to the speed of the prime mover. The speed of the engine must be maintained within a specific range for the generator to produce stable power output.
Advantages
One significant advantage of conventional generators is their affordability. They tend to have lower upfront costs compared to inverter generators. Additionally, conventional generators are widely available and come in various sizes to meet different power output requirements. They are often more powerful than their inverter counterparts, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Disadvantages
Conventional generators have some drawbacks that may affect their usability in certain situations. Firstly, they produce fluctuating power output, which can be problematic for sensitive electronics that require a stable electrical supply. The fluctuating power can potentially damage sensitive devices or cause them to malfunction.
Another disadvantage of conventional generators is their relatively higher noise levels. The mechanical components, exhaust systems, and air-cooling mechanisms of these generators contribute to their louder operation, which may not be ideal in noise-sensitive environments such as campsites or residential neighborhoods.
Furthermore, conventional generators are typically less fuel efficient than inverter generators. They consume more fuel to maintain a constant speed, even when the electrical load is minimal. This can lead to higher fuel costs and a shorter runtime per tank of fuel.
Inverter Generators
Inverter Generator Vs Generator: Inverter Generators
Inverter generators are relatively newer on the market and have gained popularity due to their advanced technology and benefits over conventional generators.
Working Principle
Inverter generators produce electricity in a three-step process: generation of three-phase alternating current (AC), conversion to direct current (DC), and inversion back to AC. This three-step process allows them to deliver a stable power output with consistent frequency and voltage, regardless of the engine speed.
In simpler terms, inverter generators generate AC power, convert it to DC power, and then convert it back to AC power with enhanced stability and control. This technology enables them to provide clean and stable power that is safe for sensitive electronics.
Advantages
One significant advantage of inverter generators is their ability to deliver clean and stable power output. This stable power is vital for sensitive electronics, such as laptops, smartphones, and medical equipment, as it eliminates the risk of damage or malfunctions caused by voltage fluctuations.
Another advantage of inverter generators is their quieter operation. The advanced technology and design of these generators allow for reduced noise levels compared to conventional generators. This makes them more suitable for use in quieter environments, such as campsites or residential areas.
Inverter generators are also known for their superior fuel efficiency. Unlike conventional generators, they have a smart throttle feature that adjusts the engine speed based on the required load. This results in reduced fuel consumption, longer runtime, and lower fuel costs.
Disadvantages
Despite their numerous advantages, inverter generators also have some drawbacks to consider. One key disadvantage is their higher initial purchase cost compared to conventional generators. The advanced technology and engineering behind inverter generators contribute to their higher price tag. However, it is important to consider the long-term cost savings in terms of fuel efficiency and potential savings from preventing damage to sensitive electronics.
Another potential drawback is their limited power output compared to conventional generators. Inverter generators are typically designed for lighter or moderate power needs and may not provide sufficient power for high-demand applications. If you require a generator for heavy-duty use, a conventional generator may be a more suitable choice.
Additionally, due to their complex design and advanced electronics, inverter generators may require more specialized maintenance and repair services, which can result in higher maintenance costs in the long run.

Power Output Differences
Inverter Generator Vs Generator: Power Output Differences.
When it comes to power output, there are a few key differences between conventional generators and inverter generators that may influence your choice.
Steady Power vs. Fluctuating Power
Conventional generators produce power output with fluctuations due to their reliance on the engine speed to determine frequency and voltage. The power output may vary depending on the load and engine speed, which can be a concern for sensitive electronics.
In contrast, inverter generators provide a stable and consistent power output regardless of the load or engine speed. They utilize advanced technology to regulate the frequency and voltage, ensuring a clean and reliable power supply for all your devices.
Noise Levels
Conventional generators are generally louder compared to inverter generators. The mechanical components, exhaust systems, and air-cooling mechanisms contribute to their noisy operation. In quiet environments or scenarios where noise is a concern, such as camping or residential areas, the lower noise levels of inverter generators can offer a more pleasant experience.
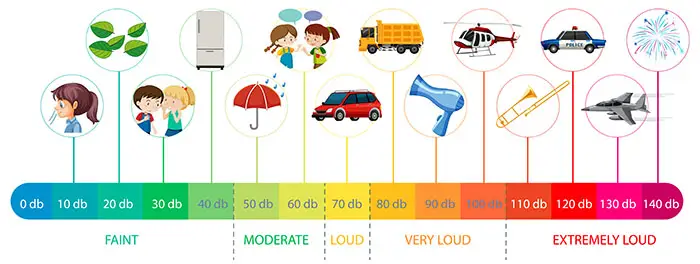
Fuel Efficiency
In terms of fuel efficiency, inverter generators have the upper hand. Their smart throttle feature adjusts the engine speed based on the required load, resulting in reduced fuel consumption. This can help extend the runtime per tank of fuel and minimize fuel costs. Conventional generators, on the other hand, tend to consume more fuel even when operating at low or minimal loads, leading to higher fuel expenses.
Portability and Size
Inverter Generator Vs Generator: Portability
The portability and size of a generator play a crucial role in determining its convenience and ease of use in different situations.
Size and Weight of Conventional Generators
Conventional generators are available in a wide range of sizes and weights, depending on their power output capacity. The larger the power capacity, the bigger and heavier the generator tends to be. This can make them more challenging to transport and maneuver, especially if you have limited physical strength or are traveling to remote locations.
Size and Weight of Inverter Generators
Inverter generators are generally more compact and lightweight compared to conventional generators. The advanced design and use of lighter materials contribute to their reduced size and weight. This makes them easier to transport and store, especially if you plan to take them on camping trips or move them frequently.
Ease of Transportation
Due to their size and weight advantages, inverter generators are generally more portable and convenient. They often come with built-in handles or wheels, making it easier to move them around or load them onto vehicles. Conventional generators, especially larger ones, may require additional accessories or assistance for transportation.
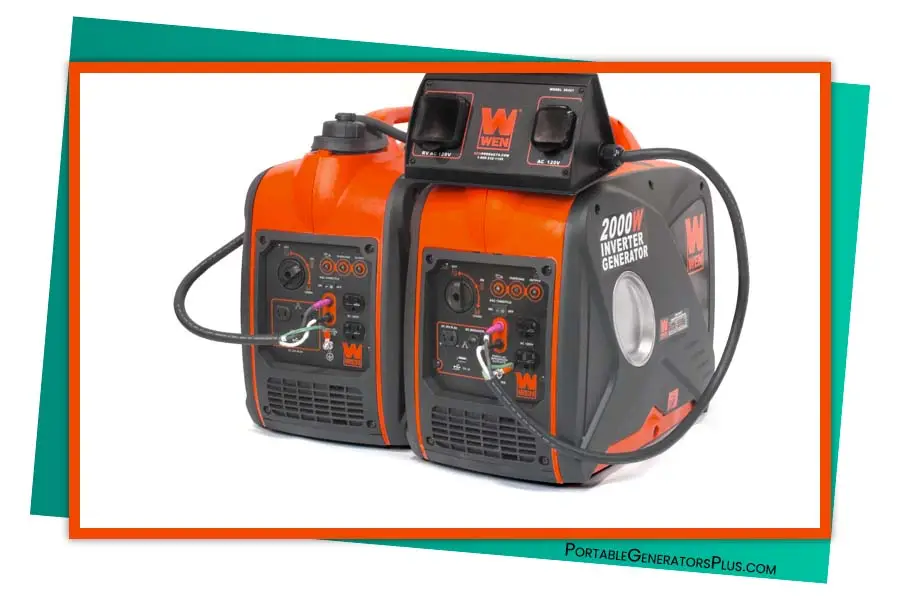
Parallel Operation
Inverter Generator Vs Generator: Parallel Definition
Parallel operation refers to the ability to connect multiple generators together and combine their power outputs. This feature can be beneficial in situations where more power is required or for redundancy purposes.
Parallel Capability of Conventional Generators
Not all conventional generators offer parallel operation capability. However, some larger models come with parallel-ready features, allowing you to connect two identical units for increased power output. This can be useful in scenarios where you need extra power for heavy-duty applications.
Parallel Capability of Inverter Generators
Inverter generators are generally designed with parallel operation capability in mind. They often come with built-in parallel-ready features, allowing you to connect two or more units together. This flexibility provides the option to scale up your power output when needed, making them ideal for various situations, from camping trips to backup power needs.

Benefits and Limitations
The ability to parallelize generators offers several benefits. It allows for increased power output to meet higher demands, provides redundancy in case one unit fails, and enables more efficient fuel consumption by only operating the necessary number of units based on the load.
However, it’s important to note that when parallelizing generators, they must be of the same brand, model, and wattage to ensure compatibility. Mixing generators from different manufacturers or models may result in operational issues and potential damage to the units.
Applications and Usage
Inverter Generator Vs Generator: Applications
Generators are used in a wide range of settings, and understanding which type is suitable for different applications can help you make the right choice.
Indoor Use
For indoor use, such as during power outages or in areas where grid electricity is unreliable, both conventional and inverter generators can be viable options. Ensure proper ventilation and follow safety guidelines when running any generator indoors to prevent carbon monoxide buildup.
Outdoor Use
Both conventional and inverter generators are suitable for outdoor use, such as camping, RVing, or outdoor events. However, inverter generators are often preferred in these scenarios due to their quieter operation and more compact size, making them more convenient to transport and use in outdoor environments.
Suitable for Sensitive Electronics
When it comes to powering sensitive electronics, such as laptops, smartphones, cameras, or medical equipment, inverter generators are the recommended choice. Their stable and clean power output eliminates the risk of damaging or malfunctioning sensitive devices due to voltage fluctuations.
Conventional generators may still be suitable for less sensitive equipment or if you plan to use voltage stabilizers or surge protectors. However, extra precautions are necessary to ensure the safety of your devices.
Cost
Inverter Generator Vs Generator: Cost factors
Cost is an essential factor to consider when purchasing a generator, as it encompasses both the initial purchase cost and the long-term cost efficiency.
Initial Purchase Cost
Conventional generators tend to have a lower initial purchase cost compared to inverter generators. This affordability makes them a popular choice for those on a tighter budget or for those who prioritize upfront savings.
Inverter generators, on the other hand, have a higher initial purchase cost due to their advanced technology, enhanced features, and improved power quality. However, the additional cost upfront may be offset by long-term savings in fuel efficiency and potential savings from preventing damage to sensitive electronics.
Maintenance and Repair Costs
Maintenance and repair costs are important factors to consider to ensure the longevity and performance of your generator throughout its lifespan.
Conventional generators typically have simpler designs and fewer electronic components, making them generally easier and more affordable to maintain and repair. Basic maintenance tasks, such as regular oil changes and air filter cleanings, can be done without the need for specialized expertise.
Inverter generators, with their advanced electronics and complex design, may require more specialized maintenance and repair services, which can result in higher costs. It is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines and seek professional assistance when needed to avoid voiding the warranty or damaging the unit.
Long-Term Cost Efficiency
While inverter generators may have a higher initial purchase cost, their fuel efficiency can result in long-term cost savings. The smart throttle feature allows them to adjust the engine speed based on the required load, minimizing fuel consumption and extending the runtime per tank of fuel.
Conventional generators, on the other hand, tend to consume more fuel even at minimal loads, leading to higher fuel expenses. However, if you’re prioritizing upfront cost savings and don’t require the benefits provided by inverter generators, a conventional generator may be a more cost-effective choice.

Maintenance and Durability
Inverter Generator Vs Generator: Durability
Proper maintenance is essential for the longevity and optimal performance of any generator. Understanding the maintenance requirements and durability of the two generator types can help you plan and allocate resources accordingly.
Required Maintenance for Conventional Generators
Conventional generators typically have simpler maintenance requirements compared to inverter generators. Common maintenance tasks include regular oil changes, filter replacements, and occasional spark plug inspections and replacements.
Following the manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines, such as checking and topping up fuel and oil levels, inspecting for leaks, cleaning the air filters, and conducting regular maintenance schedules, will help ensure the durability and reliability of your conventional generator.
Required Maintenance for Inverter Generators
Inverter generators often require more specialized maintenance due to their advanced electronics and more complex design. In addition to the standard maintenance tasks, such as oil changes and filter replacements, inverter generators may require periodic inspection and cleaning of the inverter modules, voltage regulators, and electronic components. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines and seeking professional assistance when needed is crucial to maintain the optimal performance and longevity of your inverter generator.
Lifespan and Durability
The lifespan and durability of a generator depend on several factors, including the quality of the components, adherence to maintenance schedules, and frequency and intensity of usage.
Both conventional generators and inverter generators, when properly maintained and used within their specified limits, can have long lifespans. However, the simpler design and fewer electronic components in conventional generators may provide them with a slight advantage in terms of durability. Regular maintenance and avoiding overloading or operating the generator under extreme conditions will help maximize its lifespan and ensure reliable operation.
Environmental Impact
Inverter Generator Vs Generator: How Do They impact The Enviroment?
Environmental considerations are becoming increasingly important when choosing any type of equipment. Generators are no exception, and understanding their emissions and overall environmental impact is crucial.
Emissions from Conventional Generators
Conventional generators, especially older models that may not comply with stricter emissions standards, can produce higher levels of carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and other pollutants. These emissions contribute to air pollution and can have harmful effects on both human health and the environment.
It is essential to operate conventional generators in well-ventilated areas and follow emission regulations to minimize their environmental impact. Additionally, using cleaner-burning fuels, such as low-sulfur gasoline or biodiesel, can help reduce emissions.
Emissions from Inverter Generators
Inverter generators are generally designed to comply with stricter emissions standards and incorporate technologies that reduce harmful emissions. They often feature advanced engine technologies, such as fuel injection systems and catalytic converters, to minimize emissions and enhance fuel efficiency.
While inverter generators still emit some level of pollutants, their emissions tend to be lower compared to conventional generators. As with any generator, following proper operating procedures, using appropriate fuels, and adhering to emission regulations will help minimize their environmental impact.

Environmental Friendliness
Inverter Generator Vs Conventional Generator: Earth Friendly?
In terms of overall environmental friendliness, inverter generators have the edge due to their lower emissions, fuel efficiency, and often quieter operation. The advanced technology and design of inverter generators contribute to a reduced carbon footprint and lessen their impact on the environment.
When considering the environmental impact, it’s important to factor in the usage pattern, fuel sources, and adherence to emission regulations, as these can have a significant impact on the environmental friendliness of any generator.


